Connecting Mongo Db with Asp.net Core | Mongo db with .net Core | no Sql Database
Hello & As-salam u alikum ! In this Article we will learn to create a web api using no sql database i.e "Mongodb"
Step# 1: Learn some basics of MongoDb from the below link if you are not familiar with this no sql documented database.
Click Here for Mongodb tutorial.
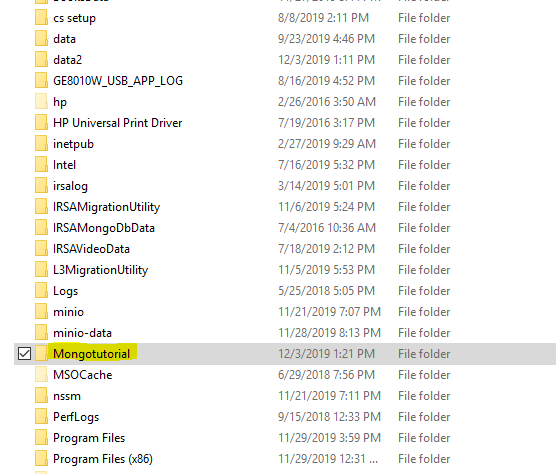
Step# 2: Create a folder as provided path C:\Mongotutorial & add a folder named as "db" in Mongotutorial folder.
Step# 3: Now Open the cmd and type the following command.
Now open Cmd & type the following command.
you will find the interface like this :
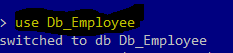
Now type below highlighted command to create database named as "db_Employee"
use the below highlighted command to make a table in the database
Add and display records in the collection or table by the following highlighted command.
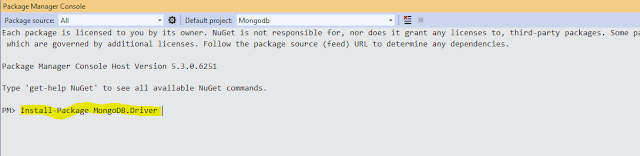
Step# 4: Now Go to the visual Studio and create a web api project and add the following package by using the package manager console.
Step# 5: Add an Entity Class in model folder named as "Employee".
Step# 6: Go to the appsetting.json file and add the connectionstring.
Step# 7: Add the below class and Interface for database connection setting.
Step# 8: Go to the startup.cs file and add the following configuration services.
Step# 9: Add the business logic in "EmployeeService" Class.
Step# 10: Goto the Startup.cs again & add the below middle-ware .
Step# 11: Now goto the home controller and paste the below code.
Conclusion :
that's all for this blog, we have successfully fetch data from Mongo db, we ll discuss more this topic in our later articles. Thank you for reading . Have a good day.
Step# 1: Learn some basics of MongoDb from the below link if you are not familiar with this no sql documented database.
Click Here for Mongodb tutorial.
Step# 2: Create a folder as provided path C:\Mongotutorial & add a folder named as "db" in Mongotutorial folder.
Step# 3: Now Open the cmd and type the following command.
mongod --dbpath C:\Mongotutorial --port 27017
When you execute this command, you will find some files created in your c:\Mongotutorial folder.
you will find the interface like this :
Now type below highlighted command to create database named as "db_Employee"
use the below highlighted command to make a table in the database
Add and display records in the collection or table by the following highlighted command.
Step# 4: Now Go to the visual Studio and create a web api project and add the following package by using the package manager console.
Step# 5: Add an Entity Class in model folder named as "Employee".
DSADASDAS
using MongoDB.Bson;
using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Mongodb.Models
{
public class Employee
{
[BsonId]
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Qualifications { get; set; }
}
}
using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Mongodb.Models
{
public class Employee
{
[BsonId]
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Qualifications { get; set; }
}
}
Step# 6: Go to the appsetting.json file and add the connectionstring.
Step# 7: Add the below class and Interface for database connection setting.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Mongodb.Models
{
interface IEmployeeDatabaseSettings
{
string EmployeeCollectionName { get; set; }
string ConnectionString { get; set; }
string DatabaseName { get; set; }
}
public class EmployeeDatabaseSettings:IEmployeeDatabaseSettings
{
public string EmployeeCollectionName { get; set; }
public string ConnectionString { get; set; }
public string DatabaseName { get; set; }
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Mongodb.Models
{
interface IEmployeeDatabaseSettings
{
string EmployeeCollectionName { get; set; }
string ConnectionString { get; set; }
string DatabaseName { get; set; }
}
public class EmployeeDatabaseSettings:IEmployeeDatabaseSettings
{
public string EmployeeCollectionName { get; set; }
public string ConnectionString { get; set; }
public string DatabaseName { get; set; }
}
}
Step# 8: Go to the startup.cs file and add the following configuration services.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Mongodb.Models;
namespace Mongodb
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<EmployeeDatabaseSettings>(
Configuration.GetSection(nameof(EmployeeDatabaseSettings)));
services.AddSingleton<IEmployeeDatabaseSettings>(sp =>
sp.GetRequiredService<IOptions<EmployeeDatabaseSettings>>().Value);
services.AddControllersWithViews();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Mongodb.Models;
namespace Mongodb
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<EmployeeDatabaseSettings>(
Configuration.GetSection(nameof(EmployeeDatabaseSettings)));
services.AddSingleton<IEmployeeDatabaseSettings>(sp =>
sp.GetRequiredService<IOptions<EmployeeDatabaseSettings>>().Value);
services.AddControllersWithViews();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
}
Step# 9: Add the business logic in "EmployeeService" Class.
using MongoDB.Driver;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Mongodb.Models
{
public class EmployeeService
{
private readonly IMongoCollection<Employee> Employee;
public EmployeeService(IEmployeeDatabaseSettings settings)
{
var client = new MongoClient(settings.ConnectionString);
var database = client.GetDatabase(settings.DatabaseName);
Employee = database.GetCollection<Employee>(settings.EmployeeCollectionName);
}
public List<Employee> Get() =>
Employee.Find(x => true).ToList();
public Employee Get(string id) =>
Employee.Find<Employee>(x => x.Id == id).FirstOrDefault();
public Employee Create(Employee x)
{
Employee.InsertOne(x);
return x;
}
public void Update(string id, Employee x) =>
Employee.ReplaceOne(y => y.Id == id, x);
public void Remove(Employee x) =>
Employee.DeleteOne(y => y.Id == x.Id);
public void Remove(string id) =>
Employee.DeleteOne(x => x.Id == id);
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Mongodb.Models
{
public class EmployeeService
{
private readonly IMongoCollection<Employee> Employee;
public EmployeeService(IEmployeeDatabaseSettings settings)
{
var client = new MongoClient(settings.ConnectionString);
var database = client.GetDatabase(settings.DatabaseName);
Employee = database.GetCollection<Employee>(settings.EmployeeCollectionName);
}
public List<Employee> Get() =>
Employee.Find(x => true).ToList();
public Employee Get(string id) =>
Employee.Find<Employee>(x => x.Id == id).FirstOrDefault();
public Employee Create(Employee x)
{
Employee.InsertOne(x);
return x;
}
public void Update(string id, Employee x) =>
Employee.ReplaceOne(y => y.Id == id, x);
public void Remove(Employee x) =>
Employee.DeleteOne(y => y.Id == x.Id);
public void Remove(string id) =>
Employee.DeleteOne(x => x.Id == id);
}
}
Step# 10: Goto the Startup.cs again & add the below middle-ware .
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Mongodb.Models;
namespace Mongodb.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly EmployeeService db;
public HomeController(EmployeeService db)
{
this.db = db;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View(db.Get());
}
public IActionResult Privacy()
{
return View();
}
[ResponseCache(Duration = 0, Location = ResponseCacheLocation.None, NoStore = true)]
public IActionResult Error()
{
return View(new ErrorViewModel { RequestId = Activity.Current?.Id ?? HttpContext.TraceIdentifier });
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Mongodb.Models;
namespace Mongodb.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly EmployeeService db;
public HomeController(EmployeeService db)
{
this.db = db;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View(db.Get());
}
public IActionResult Privacy()
{
return View();
}
[ResponseCache(Duration = 0, Location = ResponseCacheLocation.None, NoStore = true)]
public IActionResult Error()
{
return View(new ErrorViewModel { RequestId = Activity.Current?.Id ?? HttpContext.TraceIdentifier });
}
}
}
Index.cshtml:
@model IEnumerable<Mongodb.Models.Employee>
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Home Page";
}
<table class=" table table-active ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th>Qualification</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>@item.Id</td>
<td>@item.Name</td>
<td>@item.Email</td>
<td>@item.Phone</td>
<td>@item.Qualifications</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Home Page";
}
<table class=" table table-active ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th>Qualification</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>@item.Id</td>
<td>@item.Name</td>
<td>@item.Email</td>
<td>@item.Phone</td>
<td>@item.Qualifications</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
that's all for this blog, we have successfully fetch data from Mongo db, we ll discuss more this topic in our later articles. Thank you for reading . Have a good day.














0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Do not Add Spam links in the Comment Box
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home